Bars interpreting
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re conducting research or presenting data in your field, you may have to draw error bars using standard deviation. While the process can seem intimidating, it’s essential for accurately representing your data. In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about how to draw error bars using standard deviation.
When it comes to drawing error bars, it’s easy to get lost in the jargon and technical details. However, one of the most common complaints about the process is that it can be difficult to understand for those who aren’t already familiar with the concept, making it challenging to effectively communicate your findings or understand others’ research.
So, what exactly are error bars, and why should we use standard deviation when drawing them? In statistics, error bars are a visual representation of the precision of a measurement or group of measurements. In other words, they show how much variation there is around the mean or median value of the data. There are several types of error bars, but in this post, we’ll focus specifically on how to draw them using standard deviation.
To draw error bars using standard deviation, you need to first calculate the mean and standard deviation of your data. From there, you can use a graphing tool to add the error bars to your chart. The height of each bar represents the standard deviation, while the position of the bar relative to the mean value represents the precision of the measurements for that data point.
My Personal Experience Drawing Error Bars Using Standard Deviation
As a researcher who often presents data at conferences, I’ve had my fair share of experience drawing error bars using standard deviation. At first, the process can seem overwhelming, but with practice, it becomes second nature. I’ve found that using a graphing tool like Excel or Python can save time and ensure accuracy when drawing error bars.
The Benefits of Using Standard Deviation When Drawing Error Bars
While there are several ways to draw error bars, using standard deviation is one of the most common methods. One of the benefits of using standard deviation is that it provides a simple way to estimate the precision of a measurement. Additionally, it’s a relatively easy concept to understand, making it accessible to a wide range of researchers and audiences.
How to Calculate Standard Deviation
If you’re unfamiliar with how to calculate standard deviation, it’s a relatively simple process. First, find the mean of your data set. Then, for each data point, subtract the mean and square the result. Next, find the sum of those squared differences and divide it by the total number of data points minus one. Finally, take the square root of the result to get the standard deviation.
Tips for Effective Error Bar Presentation
When presenting data with error bars, it’s important to keep a few best practices in mind. First, make sure the error bars are clearly visible and labeled in your chart. Additionally, consider using color or other visual aids to differentiate between different data sets or types of error bars. Finally, make sure to explain the significance of the error bars in your data so that your audience can fully understand your findings.
Common Questions About Drawing Error Bars Using Standard Deviation
What is the Standard Error?
The standard error is a variation of the standard deviation, but it’s used to represent the precision of the mean value of a data set rather than individual measurements. To calculate the standard error, you divide the standard deviation by the square root of the sample size.
What Are the Different Types of Error Bars?
Aside from standard deviation error bars, there are several other types of error bars you may encounter, including standard error, confidence intervals, and bootstrap error bars. Each type of error bar is used to represent different aspects of the data, so it’s important to choose the appropriate type for your research question.
What Are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Drawing Error Bars?
One of the most common mistakes when drawing error bars is failing to properly label or explain them in the context of the data. Additionally, using the wrong type of error bar or failing to calculate standard deviation correctly can lead to inaccurate or misleading results.
How Can I Choose the Best Graphing Tool for My Data?
When choosing a graphing tool to draw error bars, it’s important to consider your research question, the size of your data set, and any specific requirements or preferences you may have. Some commonly used graphing tools for drawing error bars include Excel, Python, and R, among others.
Conclusion of How to Draw Error Bars Using Standard Deviation
Overall, drawing error bars using standard deviation is an essential tool for effectively communicating your data to your peers and the broader scientific community. By calculating the mean and standard deviation of your data and using a graphing tool to add error bars to your chart, you can accurately represent the precision of your findings and make informed decisions based on your results. Keep in mind the best practices and tips outlined in this post to ensure your error bars are clear and effective in conveying the significance of your research.
Gallery
Creating Error Bars On Microsoft Excel
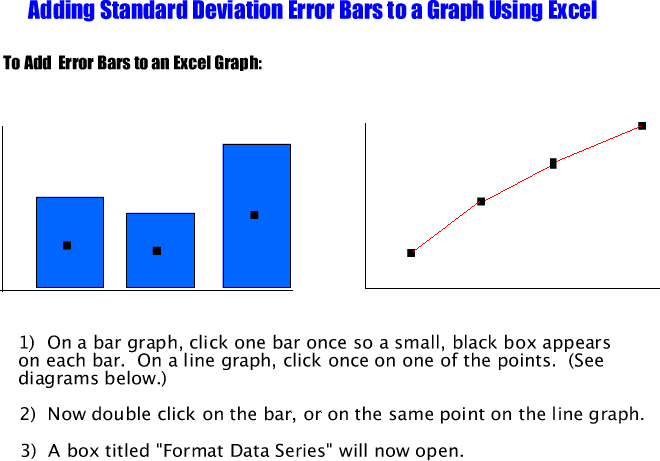
Photo Credit by: bing.com / error standard deviation bars mean using excel use calculate
Error Representation And Curvefitting

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
- Technologieser
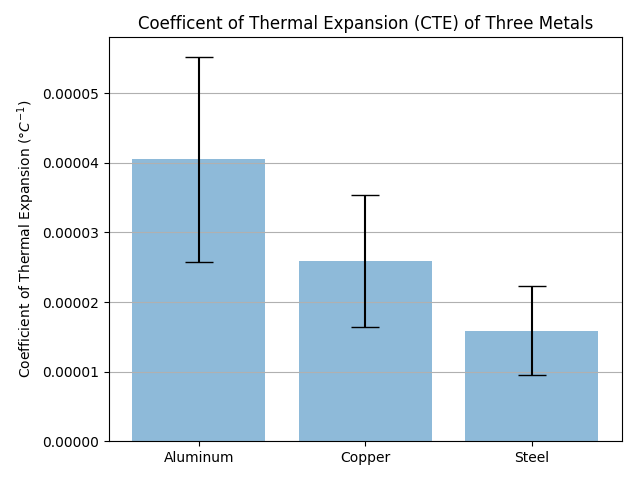
Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Interpreting Error Bars - BIOLOGY FOR LIFE | Standard Error, Teaching

Photo Credit by: bing.com / bars interpreting
How To Add Standard Deviation Bars In Numbers For Mac - Polreheavy
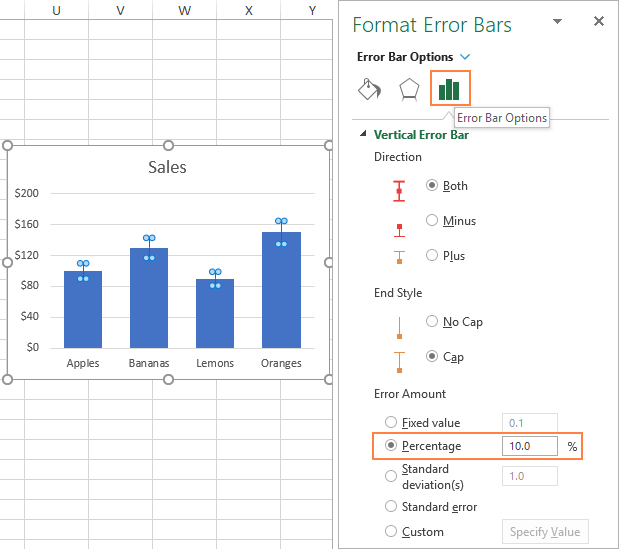
Photo Credit by: bing.com /





